MS Access Unbound Forms and VBA
Creating Unbound Forms and using VBA code behind forms.
This article will demonstrate how to create unbound forms in MS Access, both Single Form and Continuous Forms. The main goal is to provide a means of allowing users to view data without modifying it. Binding the data to the form allows users to modify or delete data from fields. Binding data also presents a locking issue when working with linked tables in SQL Server and multiple users are using copies of the Access Database front end to access the linked data.
The Single Form will use 2 methods: 1 where the form is truly not bound to the recordset or table and 1 where the form is bound to a temp table of key values from the original table\recordset to enhance navigation with unbound text boxes.
The Continuous Form will use a method where it is "unbound" to the originating table by creating a temp table and binding to the recordset and control sources at runtime. (Not truly "unbound", but as close as one can get in Access).
Creating an MS Access Unbound Single Form
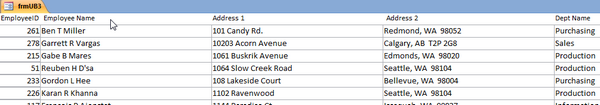
Create the SQL Server table to use in SSMS and INSERT some data from a view or other table.
create table Sales.Employees
(id int not null identity(1,1) primary key clustered,
EmployeeID int not null,
EmployeeName varchar(255) null,
AddressLine1 varchar(255) null,
AddressLine2 varchar(255) null,
DeptName varchar(255) null
)
INSERT INTO Sales.Employees
(EmployeeID,EmployeeName,AddressLine1,AddressLine2,DeptName)
SELECT EmployeeID, EmployeeName, AddressLine1 +
Case when addressLine2 IS not null THEN
' ' + AddressLine2 ELSE '' END,
City + ', ' + StateProvinceCode + ' ' + PostalCode,
DeptName
FROM dbo.vw_employees
Creating an Unbound Single Form
Click on the Create tab and select Form Design.
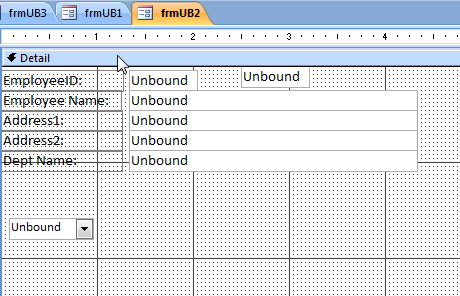
Create an Unbound form by dragging and dropping text boxes onto the new form in Form Design view. Name the boxes for the fields in the newly created SQL table, Sales.Employees.
Add a ComboBox (also unbound) to the form.
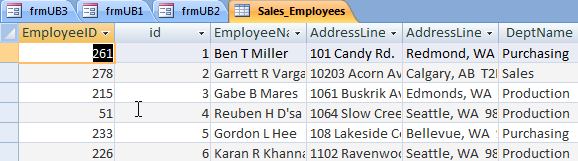
Set the RowSource of the ComboBox to: SELECT [Sales_Employees].[id], [Sales_Employees].[EmployeeID],
[Sales_Employees].[EmployeeName] FROM Sales_Employees ORDER BY [id];
Create the code
Option Compare Database
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim rs As DAO.Recordset
Public Sub getRecords()
Dim sSQL As String
sSQL = "SELECT * FROM Sales_Employees WHERE ID = " & cboEmployee.Value
Set db = CurrentDb
Set rs = db.OpenRecordset(sSQL, dbOpenDynaset, dbSeeChanges)
Me.ID = rs.Fields("ID").Value
Me.EmployeeID = rs.Fields("EmployeeID").Value
Me.EmployeeName = rs.Fields("EmployeeName").Value
Me.Address1 = rs.Fields("AddressLine1").Value
Me.Address2 = rs.Fields("AddressLine2").Value
Me.DeptName = rs.Fields("DeptName").Value
rs.Close
db.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
End Sub
Set the code of the ComboBox AfterUpdate Event (double click in the box in the Properties of the ComboBox Control) with the subprocedure getRecords.
Private Sub cboEmployee_AfterUpdate()
getRecords
End Sub
Test the form in Form View mode by clicking on the ComboBox and seeing that the record information is displayed in the TextBoxes.
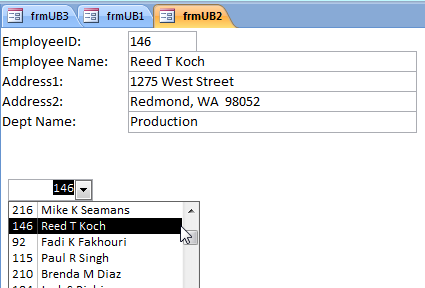
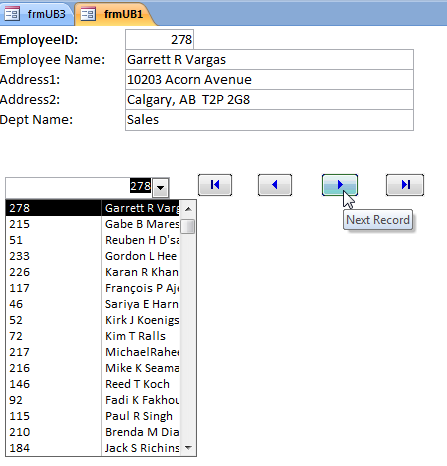
Creating a Single Form Unbound from the original Recordset
If you want to view the data using a Next or Previous button in the unbound form, you cannot. If the form is partially bound to a different datasource that is dynamically created from parts (ID, EmployeeID) of the original datasource (Sales_Employees) most of the TextBoxes on the form can remain unbound.
Create a local table for Access for the EmployeeID and ID fields from the original datasource.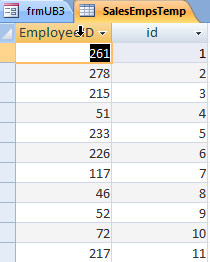
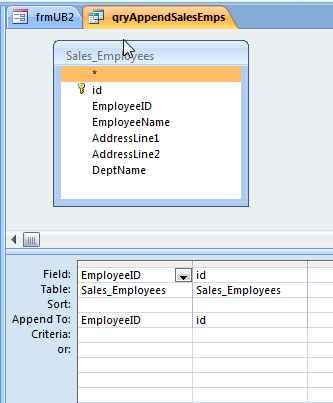
Create an Append query in Access to append the fields from the original datasource to the newly created table.
In the Form, add 4 command buttons to MoveFirst, MovePrevious, MoveNext and MoveLast.
Create the code to dynamically delete and then create the local Access table with the EmployeeID information (A DoCmd.RunSQL statement and calling the Append query). Add code to retrieve the records from the SQL datasource into the TextBoxes based on the value of the EmployeeID in the local Access table (populated and set in the FormLoad event).
Option Compare Database
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim rs As DAO.Recordset
Private Sub Form_Load()
'turn off warnings and delete then append local table SalesEmpsTemp
DoCmd.SetWarnings False
DoCmd.RunSQL "DELETE FROM SalesEmpsTemp"
DoCmd.OpenQuery "qryAppendSalesEmps", acViewNormal
DoCmd.SetWarnings True
'set the recordsource and controlsource for the ID and EmployeeID textboxes
Me.RecordSource = "Select * from SalesEmpsTemp"
ID.ControlSource = "ID"
EmployeeID.ControlSource = "EmployeeID"
'retrieve the records
getRecords
End Sub
Public Sub getRecords()
'set DAO recordset to SQL datasource and populate the TextBoxes on the form
Dim sSQL As String
sSQL = "SELECT * FROM Sales_Employees WHERE EmployeeID = " & Me.EmployeeID
Set db = CurrentDb
Set rs = db.OpenRecordset(sSQL, dbOpenDynaset, dbSeeChanges)
Me.EmployeeName = rs.Fields("EmployeeName").Value
Me.Address1 = rs.Fields("AddressLine1").Value
Me.Address2 = rs.Fields("AddressLine2").Value
Me.DeptName = rs.Fields("DeptName").Value
rs.Close
db.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
End Sub
Private Sub cboEmployee_AfterUpdate()
'make the EmployeeID and ID advance to the value in the ComboBox and retrieve the recordset
DoCmd.GoToRecord , , acGoTo, Me.cboEmployee.Value
getRecords
End Sub
Create the code for the First, Previous, Next and Last buttons
Private Sub cmdNext_Click()
On Error GoTo Err_cmdNext_Click
DoCmd.GoToRecord , , acNext
getRecords
Me.cboEmployee.Value = Me.ID
Exit_cmdNext_Click:
Exit Sub
Err_cmdNext_Click:
MsgBox Err.Description
Resume Exit_cmdNext_Click
End Sub
Private Sub cmdLast_Click()
On Error GoTo Err_cmdLast_Click
DoCmd.GoToRecord , , acLast
getRecords
Me.cboEmployee.Value = Me.ID
Exit_cmdLast_Click:
Exit Sub
Err_cmdLast_Click:
MsgBox Err.Description
Resume Exit_cmdLast_Click
End Sub
Private Sub cmdFirst_Click()
On Error GoTo Err_cmdFirst_Click
DoCmd.GoToRecord , , acFirst
getRecords
Me.cboEmployee.Value = Me.ID
Exit_cmdFirst_Click:
Exit Sub
Err_cmdFirst_Click:
MsgBox Err.Description
Resume Exit_cmdFirst_Click
End Sub
Private Sub cmdPrevious_Click()
On Error GoTo Err_cmdPrevious_Click
DoCmd.GoToRecord , , acPrevious
getRecords
Me.cboEmployee.Value = Me.ID
Exit_cmdPrevious_Click:
Exit Sub
Err_cmdPrevious_Click:
MsgBox Err.Description
Resume
Exit_cmdPrevious_Click
End Sub
Creating a Continuous Form Unbound from the Original Recordset
The Continuous Form in Access cannot be completely Unbound. It can be bound to a local Access table that contains the data (as in the previous example with the SingleForm) so that the user cannot make any changes to the original SQL datasource.
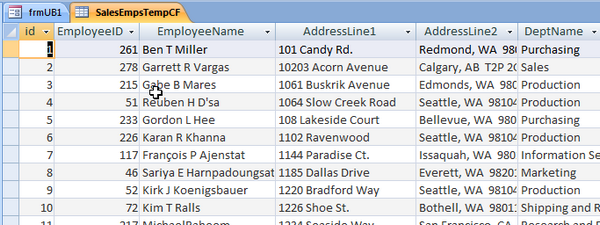
Create a new Form in FormDesign and add a FormHeader with Labels indicating the field names. Add TextBoxes named for each of the fields (EmployeeID, EmployeeName, AddressLine1, AddressLine2 and DeptName. Add code to dynamically set the controlsource of each item to the fields in the Local Access table.
Option Compare Database
Public Sub getRecords()
'turn off warnings, delete then populate the local access table with the SQL data
DoCmd.SetWarnings False
DoCmd.RunSQL "DELETE FROM SalesEmpsTempCF"
DoCmd.OpenQuery "qryAppendSalesEmpsCF", acViewNormal
DoCmd.SetWarnings True
'dynamically set the recordsource and controlsource to the Access table.
Me.RecordSource = "SELECT * FROM SalesEmpsTempCF"
Me.ID.ControlSource = "ID"
EmployeeID.ControlSource = "EmployeeID"
EmployeeName.ControlSource = "EmployeeName"
Address1.ControlSource = "AddressLine1"
Address2.ControlSource = "AddressLine2"
DeptName.ControlSource = "DeptName"
End Sub
Private Sub Form_Load()
getRecords
End Sub
View the Form in FormView